| CALY |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | CALY, DRD1IP, NSG3, calcyon neuron specific vesicular protein |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 604647; MGI: 1915816; HomoloGene: 9256; GeneCards: CALY; OMA:CALY - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 10q26.3 | Start | 133,324,072 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 133,336,935 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7|7 F4 | Start | 139,649,793 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 139,662,461 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - nucleus accumbens
- right frontal lobe
- hypothalamus
- pituitary gland
- anterior cingulate cortex
- caudate nucleus
- prefrontal cortex
- anterior pituitary
- right hemisphere of cerebellum
- amygdala
|
| | Top expressed in | - dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- primary visual cortex
- superior frontal gyrus
- hippocampus proper
- nucleus of stria terminalis
- arcuate nucleus
- central gray substance of midbrain
- ventromedial nucleus
- paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus
- dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 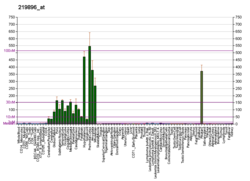 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- clathrin light chain binding
- protein-containing complex binding
- cargo receptor activity
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- plasma membrane
- integral component of plasma membrane
- cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
- cytoplasmic vesicle
- membrane
- endosome
- postsynaptic endocytic zone
- glutamatergic synapse
| | Biological process | - clathrin coat assembly
- dopamine receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of endocytosis
- endocytosis
- endosomal transport
- postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
NM_001190385
NM_001190386
NM_026769 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
NP_001177314
NP_001177315
NP_081045 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 133.32 – 133.34 Mb | Chr 7: 139.65 – 139.66 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

















