Cobalt(II,III) oxide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name cobalt(II) dicobalt(III) oxide | |
| Other names cobalt oxide, cobalt(II,III) oxide, cobaltosic oxide, tricobalt tetroxide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.780 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | Co3O4 CoO.Co2O3 |
| Molar mass | 240.80 g/mol |
| Appearance | black solid |
| Density | 6.07 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 895 °C (1,643 °F; 1,168 K) |
| Boiling point | 900 °C (1,650 °F; 1,170 K) (decomposes) |
Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Solubility | soluble (with degradation) in acids and alkalis |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | +7380·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Structure | |
| cubic | |
| Fd3m, No. 227[3] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H317, H334, H350, H411 | |
| P261, P273, P284, P304+P340, P342+P311 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |  2 0 0 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Cobalt(II,III) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Co3O4. It is one of two well characterized cobalt oxides. It is a black antiferromagnetic solid. As a mixed valence compound, its formula is sometimes written as CoIICoIII2O4 and sometimes as CoO•Co2O3.[4]
Structure
Co3O4 adopts the normal spinel structure, with Co2+ ions in tetrahedral interstices and Co3+ ions in the octahedral interstices of the cubic close-packed lattice of oxide anions.[4]
 | 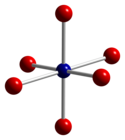 |  |
| tetrahedral coordination geometry of Co(II) | distorted octahedral coordination geometry of Co(III) | distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry of O |
Synthesis
Cobalt(II) oxide, CoO, converts to Co3O4 upon heating at around 600–700 °C in air.[4] Above 900 °C, CoO is stable.[4][5] These reactions are described by the following equilibrium:
- 2 Co3O4 ⇌ 6 CoO + O2
Applications
Cobalt(II,III) oxide is used as a blue coloring agent for pottery enamel and glass, as an alternative to cobalt(II) oxide.[6]
Cobalt(II,III) oxide is used as an electrode in some lithium-ion batteries, possibly in the form of cobalt oxide nanoparticles.
Safety
Cobalt compounds are potentially poisonous in large amounts.[7]
See also
- Cobalt(II) oxide
- Cobalt(III) oxide
References
- ^ "Cobalt(II,III) oxide 203114". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
- ^ "mp-18748: Co3O4 (cubic, Fd-3m, 227)". materialsproject.org. Retrieved 2019-12-20.
- ^ a b c d Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1118. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. p. 1520.
- ^ Frank Hamer, Janet Hamer (2004): The Potter's Dictionary of Materials and Techniques. University of Pennsylvania Press; 437 pp. ISBN 0812238109
- ^ MSDS[permanent dead link]
- v
- t
- e
- HCo(CO)4
- CoBr2
- Co(CN)2
- CoCO3
- CoC2O4
- CoCl2
- Co(ClO3)2
- Co(ClO4)2
- CoF2
- Co(HCO2)2
- CoI2
- Co(NO3)2
- Co3(PO4)2
- Co(OAc)2
- CoGeO3
- CoO
- Co(OH)2
- CoS
- Co(OCN)2
- Co(SCN)2
- CoSO4
- CoSe
- Co3P2
- CoH2
- Co(C3H6O3)2
- C
24H
48CoO
4 - C
36H
70CoO
4
- Co3O4
- CoAs
- CoCl3
- Co(NO3)3
- Co2O3
- CoF3
- Co(OH)3
- LiCoO2
- NaxCoO2
- CoF4
- Cs2CoF6
- CoC28H44
- Na3CoO4












