Coralline Crag Formation
| Coralline Crag Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Pliocene PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ | |
 Coralline Crag Formation exposed in Suffolk, England. | |
| Type | Formation |
| Unit of | Crag Group |
| Underlies | Norwich Crag Formation |
| Overlies | Thames Group (unconformity) |
| Thickness | Up to 25 metres |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sand |
| Location | |
| Region | England |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Extent |  Suffolk Suffolk |
The Coralline Crag Formation is a geological formation in England. It is a series of marine deposits found near the North Sea coast of Suffolk and characterised by bryozoan and mollusc debris. The deposit, whose onshore occurrence is mainly restricted to the area around Aldeburgh and Orford,[1][2] is a series of bioclastic calcarenites and silty sands with shell debris, deposited during a short-lived warm period at the start of the Pliocene Epoch of the Neogene Period.[3] Small areas of the rock formation are found in locations such as Boyton and Tattingstone to the south of Orford as well as offshore at Sizewell.[4]
Crag is a local word for a shelly sand. Coralline Crag has sometimes been used historically in the Suffolk coast area for building and a number of quarries exist.[2] The tower of St Peter's Church in Chillesford is one of only two built using the rock.[2]
-
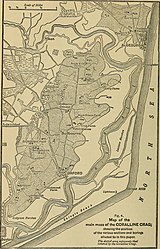 A map, published in 1898, showing the extent of Coralline Crag rocks in Suffolk
A map, published in 1898, showing the extent of Coralline Crag rocks in Suffolk -
 Quarried block of Coralline Crag, containing bryozoan fossils, in the wall of St Peter's church in Chillesford in Suffolk
Quarried block of Coralline Crag, containing bryozoan fossils, in the wall of St Peter's church in Chillesford in Suffolk -
![Fossils from the Coralline Crag. From Chatwin (1954).[5]](//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/Coralline_Crag_Fossils_Chatwin_1954.jpg/155px-Coralline_Crag_Fossils_Chatwin_1954.jpg) Fossils from the Coralline Crag. From Chatwin (1954).[5]
Fossils from the Coralline Crag. From Chatwin (1954).[5]
See also
References
- ^ British Geological Survey 1:625,000 scale geological map Bedrock Geology UK South 5th Edn 2007 NERC
- ^ a b c Suffolk, Natural England. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Brenchley, Patrick J.; Rawson, Peter F., eds. (2006). The Geology of England and Wales (2nd ed.). The Geological Society. pp. 425, 432. ISBN 1-86239-200-5.
- ^ Richmond Farm SSSI, GeoSuffolk. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Chatwin, C.P. (1954). East Anglia and adjoining areas. British Regional Geology. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. pp. 46–47.
External links
- Bryozoan fossils in the Coralline Crag rocks of Suffolk
52°07′N 1°32′E / 52.12°N 1.53°E / 52.12; 1.53
- v
- t
- e
This article related to the Neogene period is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This England-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e


![Fossils from the Coralline Crag. From Chatwin (1954).[5]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/Coralline_Crag_Fossils_Chatwin_1954.jpg/155px-Coralline_Crag_Fossils_Chatwin_1954.jpg)












