| EVI5 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | EVI5, NB4S, EVI-5, ecotropic viral integration site 5 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 602942; MGI: 104736; HomoloGene: 121902; GeneCards: EVI5; OMA:EVI5 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1p22.1 | Start | 92,508,696 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 92,792,404 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 5 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 5 F|5 52.23 cM | Start | 107,892,661 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 108,022,973 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - Achilles tendon
- sural nerve
- tendon of biceps brachii
- Epithelium of choroid plexus
- skin of hip
- testicle
- seminal vesicula
- parietal pleura
- corpus callosum
- visceral pleura
|
| | Top expressed in | - zygote
- sciatic nerve
- secondary oocyte
- epithelium of lens
- Rostral migratory stream
- saccule
- facial motor nucleus
- primary oocyte
- left lobe of liver
- cumulus cell
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 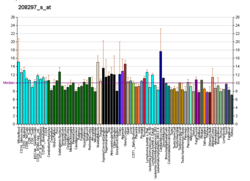
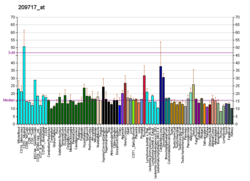 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- GTPase activator activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- cytosol
- spindle
- cytoskeleton
- nucleus
- microtubule organizing center
- endomembrane system
- Golgi apparatus
- intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
| | Biological process | - cell division
- multicellular organism development
- regulation of cilium assembly
- regulation of GTPase activity
- cell cycle
- cell population proliferation
- retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi
- regulation of vesicle fusion
- intracellular protein transport
- activation of GTPase activity
- positive regulation of GTPase activity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001308248
NM_005665
NM_001350197
NM_001350198
NM_001377210
|
|---|
NM_001377211
NM_001377212
NM_001377213 |
| |
|---|
NM_007964
NM_001378824
NM_001378825 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001295177
NP_005656
NP_001337126
NP_001337127
NP_001364139
|
|---|
NP_001364140
NP_001364141
NP_001364142 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 92.51 – 92.79 Mb | Chr 5: 107.89 – 108.02 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|




















