Early European Farmers
Early European Farmers (EEF)[a] were a group of the Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF) who brought agriculture to Europe and Northwest Africa. The Anatolian Neolithic Farmers were an ancestral component, first identified in farmers from Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor) in the Neolithic, and outside in Europe and Northwest Africa, they also existed in Iranian Plateau, South Caucasus, Mesopotamia and Levant. Although the spread of agriculture from the Middle East to Europe has long been recognised through archaeology, it is only recent advances in archaeogenetics that have confirmed that this spread was strongly correlated with a migration of these farmers, and was not just a cultural exchange.
The earliest farmers in Anatolia derived most (80–90%) of their ancestry from the regions local hunter-gatherers, with minor Levantine and Caucasus-related ancestry.[1] The Early European Farmers moved into Europe from Anatolia through Southeast Europe from around 7,000 BC, gradually spread north and westwards, and reached Northwest Africa via the Iberian Peninsula. Genetic studies have confirmed that the later Farmers of Europe generally have also a minor contribution from Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHGs), with significant regional variation. European farmer and hunter-gatherer populations coexisted and traded in some locales, although evidence suggests that the relationship was not always peaceful. Over the course of the next 4,000 years or so, Europe was transformed into agricultural communities, with WHGs being effectively replaced across Europe. During the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Age, people who had Western Steppe Herder (WSH) ancestry moved into Europe and mingled with the EEF population; these WSH, originating from the Yamnaya culture of the Pontic steppe of Eastern Europe, probably spoke Indo-European languages. EEF ancestry is common in modern European and Northwest African populations, with EEF ancestry highest in Southern Europeans, especially Sardinians and Basque people
A distinct group of the Anatolian Neolithic Farmers spread into the east of Anatolia, and left a considerable genetic legacy in Iranian Plateau, South Caucasus, Levant (during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B) and Mesopotamia. They also have a minor role in the ethnogenesis of WSHs of Yamnaya culture.
The ANF ancestry is found in substantial levels in contemporary European, West Asian and North African populations, and also found in Central and South Asian populations (through Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex and Corded Ware Culture) with more lower levels.
Overview
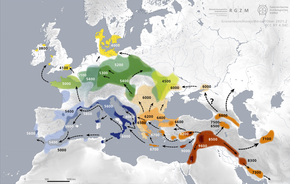
Populations of the Anatolian Neolithic derived most of their ancestry from the Anatolian hunter-gatherers (AHG), with a minor geneflow from Iranian/Caucasus and Levantine related sources, suggesting that agriculture was adopted in situ by these hunter-gatherers and not spread by demic diffusion into the region.[1] Ancestors of AHGs and EEFs are believed to have split off from Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHGs) between 45kya to 26kya during the Last Glacial Maximum, and to have split from Caucasian Hunter-Gatherers (CHGs) between 25kya to 14kya.[2]
Genetic studies demonstrate that the introduction of farming to Europe in the 7th millennium BC was associated with a mass migration of people from Northwest Anatolia to Southeast Europe,[3] which resulted in the replacement of almost all (c. 98%) of the local Balkan hunter-gatherer gene pool with ancestry from Anatolian farmers.[4][5][6] In the Balkans, the EEFs appear to have divided into two wings, who expanded further west into Europe along the Danube (Linear Pottery culture) or the western Mediterranean (Cardial Ware). Large parts of Northern Europe and Eastern Europe nevertheless remained unsettled by EEFs. During the Middle Neolithic there was a largely male-driven resurgence of WHG ancestry among many EEF-derived communities, leading to increasing frequencies of the hunter-gatherer paternal haplogroups among them.
Around 7,500 years ago. Iberian EEFs migrated into Northwest Africa, bringing farming to the region.[7]
The most common paternal haplogroup among EEFs was haplogroup G2a, while haplogroups E1b1 and R1b have also been found.[8] Their maternal haplogroups consisted mainly of West Eurasian lineages including haplogroups H2, I, and T2, however significant numbers of central European farmers belonged to East Asian maternal lineage N9a, which is almost non-existent in modern Europeans, but common in East Asia.[8][9][10]
During the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Age, the EEF-derived cultures of Europe were overwhelmed by successive migrations of Western Steppe Herders (WSHs) from the Pontic–Caspian steppe, who carried roughly equal amounts of Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) and Caucasus Hunter-Gatherer (CHG) ancestries. These migrations led to EEF paternal DNA lineages in Europe being almost entirely replaced with WSH-derived paternal DNA (mainly subclades of EHG-derived R1b and R1a). EEF maternal DNA (mainly haplogroup N) was also substantially replaced, being supplanted by steppe lineages,[11][12] suggesting the migrations involved both males and females from the steppe.[13][14]
A 2017 study found that Bronze Age European with steppe ancestry had elevated EEF ancestry on the X chromosome, suggesting a sex bias, in which Steppe ancestry was inherited by more male than female ancestors.[15] However, this study's results could not be replicated in a follow-up study by Iosif Lazaridis and David Reich, suggesting that the authors had mis-measured the admixture proportions of their sample.[16]
EEF ancestry remains widespread throughout Europe, ranging from about 60% near the Mediterranean Sea (with a peak of 65% [17] in the island of Sardinia) and diminishing northwards to about 10% in northern Scandinavia. According to more recent studies the highest EEF ancestry found in modern Europeans ranges from 67% to over 80% in modern Sardinians, Italians, and Iberians, with the lowest EEF ancestry found in modern Europeans ranging around 35-40% in modern Finns, Lithuanians and Latvians.[18][19] EEF ancestry is also prominent in living Northwest Africans like Moroccans and Algerians.[20]
Physical appearance and allele frequency

European hunter-gatherers were much taller than EEFs, and the replacement of European hunter-gatherers by EEFs resulted in a dramatic decrease in genetic height throughout Europe. During the later phases of the Neolithic, height increased among European farmers, probably due to increasing admixture with hunter-gatherers. During the Late Neolithic and Bronze Age, further reductions of EEF ancestry in Europe due to migrations of peoples with steppe-related ancestry is associated with further increases in height.[21] High frequencies of EEF ancestry in Southern Europe might partly explain the shortness of Southern Europeans as compared to Northern Europeans, who carry increased levels of steppe-related ancestry.[22]
The Early European Farmers are believed to have been mostly dark haired and dark eyed, and light skinned,[23][24] although darker than most modern Europeans.[25] A study on different EEF remains throughout Europe concluded that they had "intermediate to light skin complexion".[26] A 2024 study found that risk alleles for mood-related phenotypes are enriched in the ancestry of Neolithic farmers.[27]
Subsistence
EEFs and their Anatolian forebears kept taurine cattle,[28] pigs,[29] sheep and goats,[30] as livestock, and planted cereal crops like wheat.[31]
Social organisation
Genetic analysis of individuals found in Neolithic tombs suggests that least some EEF peoples were patrilineal (tracing descent through the male line), with the tombs occupants mostly consisting of the male descendants of a single male common ancestor and their children, as well as their wives which were genetically unrelated to their husbands, suggesting female exogamy.[32][33]
See also
References
- ^ a b Krause, Johannes; Jeong, Choongwon; Haak, Wolfgang; Posth, Cosimo; Stockhammer, Philipp W.; Mustafaoğlu, Gökhan; Fairbairn, Andrew; Bianco, Raffaela A.; Julia Gresky (19 March 2019). "Late Pleistocene human genome suggests a local origin for the first farmers of central Anatolia". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 1218. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.1218F. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09209-7. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 6425003. PMID 30890703.
- ^ Marchi, Nina; Winkelbach, Laura; Schulz, Ilektra; Brami, Maxime; Hofmanová, Zuzana; Blöcher, Jens; Reyna-Blanco, Carlos S.; Diekmann, Yoan; Thiéry, Alexandre; Kapopoulou, Adamandia; Link, Vivian; Piuz, Valérie; Kreutzer, Susanne; Figarska, Sylwia M.; Ganiatsou, Elissavet (May 2022). "The genomic origins of the world's first farmers". Cell. 185 (11): 1842–1859.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.008. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 9166250. PMID 35561686.
- ^ Lazaridis, Iosif; Nadel, Dani; Rollefson, Gary; Merrett, Deborah C.; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; Fernandes, Daniel; Novak, Mario; Gamarra, Beatriz; Sirak, Kendra; Connell, Sarah; Stewardson, Kristin; Harney, Eadaoin; Fu, Qiaomei; Gonzalez-Fortes, Gloria (8 August 2016). "Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East". Nature. 536 (7617): 419–424. Bibcode:2016Natur.536..419L. doi:10.1038/nature19310. PMC 5003663. PMID 27459054.
- ^ Mathieson et al. 2018.
- ^ Curry, Andrew (August 2019). "The first Europeans weren't who you might think". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 19 March 2021.
- ^ Spinney, Laura (1 July 2020). "When the First Farmers Arrived in Europe, Inequality Evolved". Scientific American.
- ^ Simões, Luciana G.; Günther, Torsten; Martínez-Sánchez, Rafael M.; Vera-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos; Iriarte, Eneko; Rodríguez-Varela, Ricardo; Bokbot, Youssef; Valdiosera, Cristina; Jakobsson, Mattias (15 June 2023). "Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant". Nature. 618 (7965): 550–556. Bibcode:2023Natur.618..550S. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06166-6. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 10266975. PMID 37286608.
- ^ a b Manco, Jean (2016). Ancestral Journeys: The Peopling of Europe from the First Venturers to the Vikings (Revised and Updated ed.). Thames & Hudson. p. 98-100. ISBN 978-0-500-77290-4.
- ^ Guba, Zsuzsanna; Hadadi, Éva; Major, Ágnes; Furka, Tünde; Juhász, Emese; Koós, Judit; Nagy, Károly; Zeke, Tamás (November 2011). "HVS-I polymorphism screening of ancient human mitochondrial DNA provides evidence for N9a discontinuity and East Asian haplogroups in the Neolithic Hungary". Journal of Human Genetics. 56 (11): 784–796. doi:10.1038/jhg.2011.103. ISSN 1435-232X. PMID 21918529. S2CID 20827921.
- ^ Derenko, Miroslava; Malyarchuk, Boris; Grzybowski, Tomasz; Denisova, Galina; Rogalla, Urszula; Perkova, Maria; Dambueva, Irina; Zakharov, Ilia (21 December 2010). "Origin and Post-Glacial Dispersal of Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups C and D in Northern Asia". PLOS ONE. 5 (12): e15214. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...515214D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015214. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3006427. PMID 21203537.
- ^ Crabtree, Pam J.; Bogucki, Peter (25 January 2017). European Archaeology as Anthropology: Essays in Memory of Bernard Wailes. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-934536-90-2.p.55: "In addition, uniparental markers changed suddenly as mtDNA N1a and Y haplogroup G2a, which had been very common in the EEF agricultural population, were replaced by Y haplogroups R1a and R1b and by a variety of mtDNA haplogroups typical of the Steppe Yamnaya population. The uniparental markers show that the migrants included both men and women from the steppes."
- ^ Översti, Sanni; Majander, Kerttu; Salmela, Elina; Salo, Kati; Arppe, Laura; Belskiy, Stanislav; Etu-Sihvola, Heli; Laakso, Ville; Mikkola, Esa; Pfrengle, Saskia; Putkonen, Mikko; Taavitsainen, Jussi-Pekka; Vuoristo, Katja; Wessman, Anna; Sajantila, Antti; Oinonen, Markku; Haak, Wolfgang; Schuenemann, Verena J.; Krause, Johannes; Palo, Jukka U.; Onkamo, Päivi (15 November 2019). "Human mitochondrial DNA lineages in Iron-Age Fennoscandia suggest incipient admixture and eastern introduction of farming-related maternal ancestry". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 16883. Bibcode:2019NatSR...916883O. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-51045-8. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6858343. PMID 31729399. "The subsequent spread of Yamnaya-related people and Corded Ware Culture in the late Neolithic and Bronze Age were accompanied with the increase of haplogroups I, U2 and T1 in Europe (See8 and references therein)."
- ^ Juras et al. 2018: We identified, for the first time in ancient populations, the rare mitochondrial haplogroup X4 in two Bronze Age Catacomb culture-associated individuals. Genetic similarity analyses show close maternal genetic affinities between populations associated with both eastern and Baltic Corded Ware culture, and the Yamnaya horizon, in contrast to larger genetic differentiation between populations associated with western Corded Ware culture and the Yamnaya horizon. This indicates that females with steppe ancestry contributed to the formation of populations associated with the eastern Corded Ware culture while more local people, likely of Neolithic farmer ancestry, contributed to the formation of populations associated with western Corded Ware culture.
- ^ Olalde et al. 2019, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Goldberg et al. 2017.
- ^ Lazaridis, Iosif; Reich, David (5 May 2017). "Failure to replicate a genetic signal for sex bias in the steppe migration into central Europe". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114 (20): E3873–E3874. Bibcode:2017PNAS..114E3873L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704308114. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 5441797. PMID 28476764.
- ^ Fernandes, Daniel M.; et al. (2020). "The spread of steppe and Iranian-related ancestry in the islands of the western Mediterranean". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 4 (3): 334–345. Bibcode:2020NatEE...4..334F. doi:10.1038/s41559-020-1102-0. PMC 7080320. PMID 32094539.
- ^ Allentoft, Morten E.; Sikora, Martin; Refoyo-Martínez, Alba; Irving-Pease, Evan K.; Fischer, Anders; Barrie, William; Ingason, Andrés; Stenderup, Jesper; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Pearson, Alice; Mota, Barbara; Paulsson, Bettina Schulz; Halgren, Alma; Macleod, Ruairidh; Jørkov, Marie Louise Schjellerup (5 May 2022), Population Genomics of Stone Age Eurasia, pp. 2022.05.04.490594, doi:10.1101/2022.05.04.490594, S2CID 248563160
- ^ Christina, Clemente, Florian Unterlaender, Martina Dolgova, Olga Amorim, Carlos Eduardo G. Coroado-Santos, Francisco Neuenschwander, Samuel Ganiatsou, Elissavet Davalos, Diana I. Cruz Anchieri, Lucas Michaud, Frederic Winkelbach, Laura Bloecher, Jens Cardenas, Yami Ommar Arizmendi da Mota, Barbara Sousa Kalliga, Eleni Souleles, Angelos Kontopoulos, Ioannis Karamitrou-Mentessidi, Georgia Philaniotou, Olga Sampson, Adamantios Theodorou, Dimitra Tsipopoulou, Metaxia Akamatis, Ioannis Halstead, Paul Kotsakis, Kostas Urem-Kotsou, Dushka Panagiotopoulos, Diamantis Ziota, Christina Triantaphyllou, Sevasti Delaneau, Olivier Jensen, Jeffrey D. Victor Moreno-Mayar, J. Burger, Joachim Sousa, Vitor C. Lao, Oscar Malaspinas, Anna-Sapfo Papageorgopoulou (2021). The genomic history of the Aegean palatial civilizations. p. 41. OCLC 1263227362.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Serra-Vidal, Gerard; Lucas-Sanchez, Marcel; Fadhlaoui-Zid, Karima; Bekada, Asmahan; Zalloua, Pierre; Comas, David (November 2019). "Heterogeneity in Palaeolithic Population Continuity and Neolithic Expansion in North Africa". Current Biology. 29 (22): 3953–3959.e4. Bibcode:2019CBio...29E3953S. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.09.050. PMID 31679935.
- ^ Martiniano et al. 2017, p. 9.
- ^ Mathieson et al. 2015, p. 4. "[R]esults suggest that the modern South-North gradient in height across Europe is due to both increased steppe ancestry in northern populations, and selection for decreased height in Early Neolithic migrants to southern Europe."
- ^ Reich 2018, p. 96
- ^ Lalueza-Fox, Carles (1 February 2022). Inequality: A Genetic History. MIT Press. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-262-04678-7. "p.29: "Physically, early farmers from Anatolia were different from those foragers; they had brown eyes but fair skin...."
- ^ Wang, Ke; Prüfer, Kay; Krause-Kyora, Ben; Childebayeva, Ainash; Schuenemann, Verena J.; Coia, Valentina; Maixner, Frank; Zink, Albert; Schiffels, Stephan; Krause, Johannes (16 August 2023). "High-coverage genome of the Tyrolean Iceman reveals unusually high Anatolian farmer ancestry". Cell Genomics. 3 (9): 100377. doi:10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100377. ISSN 2666-979X. PMC 10504632. PMID 37719142.
- ^ Marchi, Nina; Winkelbach, Laura; Schulz, Ilektra; Brami, Maxime; Hofmanová, Zuzana; Blöcher, Jens; Reyna-Blanco, Carlos S.; Diekmann, Yoan; Thiéry, Alexandre; Kapopoulou, Adamandia; Link, Vivian; Piuz, Valérie; Kreutzer, Susanne; Figarska, Sylwia M.; Ganiatsou, Elissavet (May 2022). "The genomic origins of the world's first farmers". Cell. 185 (11): 1842–1859.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.008. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 9166250. PMID 35561686.
We find that the vast majority of early farmers in our dataset had intermediate to light skin complexion
- ^ Irving-Pease, Evan K.; Refoyo-Martínez, Alba; Barrie, William; Ingason, Andrés; Pearson, Alice; Fischer, Anders; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Halgren, Alma S.; Macleod, Ruairidh; Demeter, Fabrice; Henriksen, Rasmus A.; Vimala, Tharsika; McColl, Hugh; Vaughn, Andrew H.; Speidel, Leo (January 2024). "The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians". Nature. 625 (7994): 312–320. Bibcode:2024Natur.625..312I. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06705-1. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 10781624. PMID 38200293.
- ^ Scheu, Amelie; Powell, Adam; Bollongino, Ruth; Vigne, Jean-Denis; Tresset, Anne; Çakırlar, Canan; Benecke, Norbert; Burger, Joachim (December 2015). "The genetic prehistory of domesticated cattle from their origin to the spread across Europe". BMC Genetics. 16 (1): 54. doi:10.1186/s12863-015-0203-2. ISSN 1471-2156. PMC 4445560. PMID 26018295.
- ^ Frantz, Laurent A. F.; Haile, James; Lin, Audrey T.; Scheu, Amelie; Geörg, Christina; Benecke, Norbert; Alexander, Michelle; Linderholm, Anna; Mullin, Victoria E.; Daly, Kevin G.; Battista, Vincent M.; Price, Max; Gron, Kurt J.; Alexandri, Panoraia; Arbogast, Rose-Marie (27 August 2019). "Ancient pigs reveal a near-complete genomic turnover following their introduction to Europe". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (35): 17231–17238. Bibcode:2019PNAS..11617231F. doi:10.1073/pnas.1901169116. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6717267. PMID 31405970.
- ^ Gillis, Rosalind E.; Gaastra, Jane S.; Linden, Marc Vander; Vigne, Jean-Denis (2 January 2022). "A Species Specific Investigation Into Sheep and Goat Husbandry During the Early European Neolithic". Environmental Archaeology. 27 (1): 8–19. Bibcode:2022EnvAr..27....8G. doi:10.1080/14614103.2019.1615214. ISSN 1461-4103.
- ^ Brami, Maxime; Heyd, Volker (January 2011). "The origins of Europe's first farmers: The role of Hacılar and Western Anatolia, fifty years on". Praehistorische Zeitschrift. 86 (2). doi:10.1515/pz.2011.011. ISSN 0079-4848.
- ^ Fowler, Chris; Olalde, Iñigo; Cummings, Vicki; Armit, Ian; Büster, Lindsey; Cuthbert, Sarah; Rohland, Nadin; Cheronet, Olivia; Pinhasi, Ron; Reich, David (27 January 2022). "A high-resolution picture of kinship practices in an Early Neolithic tomb". Nature. 601 (7894): 584–587. Bibcode:2022Natur.601..584F. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04241-4. ISSN 0028-0836. PMC 8896835. PMID 34937939.
- ^ Seersholm, Frederik Valeur; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Koelman, Julia; Blank, Malou; Svensson, Emma M.; Staring, Jacqueline; Fraser, Magdalena; Pinotti, Thomaz; McColl, Hugh; Gaunitz, Charleen; Ruiz-Bedoya, Tatiana; Granehäll, Lena; Villegas-Ramirez, Berenice; Fischer, Anders; Price, T. Douglas (August 2024). "Repeated plague infections across six generations of Neolithic Farmers". Nature. 632 (8023): 114–121. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07651-2. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 11291285. PMID 38987589.
Bibliography
- Alt, Kurt W.; et al. (7 February 2020). "A massacre of early Neolithic farmers in the high Pyrenees at Els Trocs, Spain". Scientific Reports. 10 (2131). Nature Research: 2131. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.2131A. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58483-9. PMC 7005801. PMID 32034181.
- Brace, Selina; et al. (15 April 2019). "Ancient genomes indicate population replacement in Early Neolithic Britain". Nature Ecology and Evolution. 3 (5). Nature Research: 765–771. Bibcode:2019NatEE...3..765B. doi:10.1038/s41559-019-0871-9. PMC 7005801. PMID 32034181.
- Brunel, Samantha; et al. (9 June 2020). "Ancient genomes from present-day France unveil 7,000 years of its demographic history". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (23). National Academy of Sciences: 12791–12798. Bibcode:2020PNAS..11712791B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1918034117. PMC 7293694. PMID 32457149.
- Cassidy, Lara M.; et al. (17 June 2020). "A dynastic elite in monumental Neolithic society". Nature. 582 (7812). Nature Research: 384–388. Bibcode:2020Natur.582..384C. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2378-6. PMC 7116870. PMID 32555485. S2CID 219729757.
- Fregel, Rosa; et al. (26 June 2018). "Ancient genomes from North Africa evidence prehistoric migrations to the Maghreb from both the Levant and Europe". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (26). National Academy of Sciences: 6774–6779. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115.6774F. doi:10.1073/pnas.1800851115. PMC 6042094. PMID 29895688.
- Simões, Luciana G; et al. (7 June 2023). "Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant". Nature. 618 (7965). Nature Research: 550–556. Bibcode:2023Natur.618..550S. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06166-6. PMC 10266975. PMID 37286608.
- Goldberg, Amy; et al. (7 March 2017). "Ancient X chromosomes reveal contrasting sex bias in Neolithic and Bronze Age Eurasian migrations". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 114 (10). National Academy of Sciences: 2657–2662. Bibcode:2017PNAS..114.2657G. doi:10.1073/pnas.1616392114. PMC 5347611. PMID 28223527.
- Haak, Wolfgang; et al. (2 March 2015). "Massive migration from the steppe was a source for Indo-European languages in Europe". Nature. 522 (7555). Nature Research: 207–211. arXiv:1502.02783. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..207H. doi:10.1038/nature14317. PMC 5048219. PMID 25731166.
- Jones, Eppie R.; et al. (16 November 2015). "Upper Palaeolithic genomes reveal deep roots of modern Eurasians". Nature Communications. 6 (8912). Nature Research: 8912. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.8912J. doi:10.1038/ncomms9912. PMC 4660371. PMID 26567969.
- Jones, Eppie R.; et al. (20 February 2017). "The Neolithic Transition in the Baltic Was Not Driven by Admixture with Early European Farmers". Current Biology. 27 (4). Cell Press: 576–582. Bibcode:2017CBio...27..576J. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.12.060. PMC 5321670. PMID 28162894.
- Juras, Anna; et al. (2 August 2018). "Mitochondrial genomes reveal an east to west cline of steppe ancestry in Corded Ware populations". Scientific Reports. 8 (11603). Nature Research: 11603. Bibcode:2018NatSR...811603J. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-29914-5. PMC 6072757. PMID 30072694.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; et al. (17 September 2014). "Ancient human genomes suggest three ancestral populations for present-day Europeans". Nature. 513 (7518). Nature Research: 409–413. arXiv:1312.6639. Bibcode:2014Natur.513..409L. doi:10.1038/nature13673. PMC 4170574. PMID 25230663.
- Lipson, Mark; et al. (8 November 2017). "Parallel palaeogenomic transects reveal complex genetic history of early European farmers". Nature. 551 (7680). Nature Research: 368–372. Bibcode:2017Natur.551..368L. doi:10.1038/nature24476. PMC 5973800. PMID 29144465.
- Malmström, Helena; et al. (19 January 2015). "Ancient mitochondrial DNA from the northern fringe of the Neolithic farming expansion in Europe sheds light on the dispersion process". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 370 (1660). Royal Society. doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0373. PMC 4275881. PMID 25487325.
- Marcus, Joseph H.; et al. (24 February 2020). "Genetic history from the Middle Neolithic to present on the Mediterranean island of Sardinia". Nature Communications. 11 (939). Nature Research: 939. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11..939M. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-14523-6. PMC 7039977. PMID 32094358.
- Martiniano, Rui; et al. (27 July 2017). "The population genomics of archaeological transition in west Iberia: Investigation of ancient substructure using imputation and haplotype-based methods". PLOS Genetics. 13 (7). PLOS: e1006852. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1006852. PMC 5531429. PMID 28749934.
- Mathieson, Iain; et al. (23 November 2015). "Genome-wide patterns of selection in 230 ancient Eurasians". Nature. 528 (7583). Nature Research: 499–503. Bibcode:2015Natur.528..499M. doi:10.1038/nature16152. PMC 4918750. PMID 26595274.
- Mathieson, Iain; et al. (21 February 2018). "The genomic history of southeastern Europe". Nature. 555 (7695). Nature Research: 197–203. Bibcode:2018Natur.555..197M. doi:10.1038/nature25778. PMC 6091220. PMID 29466330.
- Olalde, Iñigo; et al. (2 September 2015). "A Common Genetic Origin for Early Farmers from Mediterranean Cardial and Central European LBK Cultures". PLOS Genetics. 32 (12). PLOS: 3132–3142. doi:10.1093/molbev/msv181. PMC 4652622. PMID 26337550.
- Olalde, Iñigo; et al. (15 March 2019). "The genomic history of the Iberian Peninsula over the past 8000 years". Science. 363 (6432). American Association for the Advancement of Science: 1230–1234. Bibcode:2019Sci...363.1230O. doi:10.1126/science.aav4040. PMC 6436108. PMID 30872528.
- Rivollat, Maïté; et al. (29 May 2020). "Ancient genome-wide DNA from France highlights the complexity of interactions between Mesolithic hunter-gatherers and Neolithic farmers". Science. 6 (22). American Association for the Advancement of Science: eaaz5344. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.5344R. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaz5344. PMC 7259947. PMID 32523989.
- Saag, Lehti; et al. (24 July 2017). "Extensive Farming in Estonia Started through a Sex-Biased Migration from the Steppe". Current Biology. 27 (14). Cell Press: 2185–2193. Bibcode:2017CBio...27E2185S. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2017.06.022. PMID 28712569.
- Sánchez-Quinto, Federico; et al. (7 May 2019). "Megalithic tombs in western and northern Neolithic Europe were linked to a kindred society". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (19). National Academy of Sciences: 9469–9474. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116.9469S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1818037116. PMC 6511028. PMID 30988179.
Further reading
- Anthony, David (Spring–Summer 2019). "Archaeology, Genetics, and Language in the Steppes: A Comment on Bomhard". Journal of Indo-European Studies. 47 (1–2). Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- Anthony, David W. (2019b). "Ancient DNA, Mating Networks, and the Anatolian Split". In Serangeli, Matilde; Olander, Thomas (eds.). Dispersals and Diversification: Linguistic and Archaeological Perspectives on the Early Stages of Indo-European. BRILL. pp. 21–54. ISBN 978-9004416192.
- González-Fortes, Gloria; et al. (19 June 2017). "Paleogenomic Evidence for Multi-generational Mixing between Neolithic Farmers and Mesolithic Hunter-Gatherers in the Lower Danube Basin". Current Biology. 27 (12). Cell Press: 1801–1810. Bibcode:2017CBio...27E1801G. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.023. PMC 5483232. PMID 28552360.
- Hofmanová, Zuzana; et al. (21 June 2016). "Early farmers from across Europe directly descended from Neolithic Aegeans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (25). National Academy of Sciences: 6886–6891. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.6886H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1523951113. PMC 4922144. PMID 27274049.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; et al. (25 July 2016). "Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East". Nature. 536 (7617). Nature Research: 419–424. Bibcode:2016Natur.536..419L. doi:10.1038/nature19310. PMC 5003663. PMID 27459054.
- Lazaridis, Iosif (December 2018). "The evolutionary history of human populations in Europe". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 53. Elsevier: 21–27. arXiv:1805.01579. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2018.06.007. PMID 29960127. S2CID 19158377.
- Nikitin, Alexey G.; et al. (20 December 2019). "Interactions between earliest Linearbandkeramik farmers and central European hunter gatherers at the dawn of European Neolithization". Scientific Reports. 9 (19544). Nature Research: 19544. Bibcode:2019NatSR...919544N. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-56029-2. PMC 6925266. PMID 31863024.
- Outram, Alan K.; Bogaard, Amy (2019). Subsistence and Society in Prehistory: New Directions in Economic Archaeology. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781316415177. ISBN 9781107128774. S2CID 211576479.
- Reich, David (2018). Who We are and how We Got Here: Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-882125-0.
- Shennan, Stephen (2018). The First Farmers of Europe: An Evolutionary Perspective. Cambridge World Archaeology. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108386029. ISBN 9781108422925.
Notes
- ^ Sometimes called as First European Farmers, Neolithic European Farmers or Ancient Aegean Farmers
- v
- t
- e
by region
by group
- Europe
- Azerbaijanis
- Jews
- Turks
- MENA
- South Asia
- East Asia
- Southeast Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa
 Category
Category











