| PLEKHB2 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
3AJ4, 3VIA |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PLEKHB2, EVT2, pleckstrin homology domain containing B2 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 618452; MGI: 2385825; HomoloGene: 9938; GeneCards: PLEKHB2; OMA:PLEKHB2 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 2q21.1 | Start | 131,104,847 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 131,353,709 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 1|1 B | Start | 34,889,057 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 34,918,661 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - pons
- endothelial cell
- superior vestibular nucleus
- inferior ganglion of vagus nerve
- Pars compacta
- Brodmann area 23
- cerebellar vermis
- spinal ganglia
- lateral nuclear group of thalamus
- pars reticulata
|
| | Top expressed in | - choroid plexus of fourth ventricle
- medulla oblongata
- superior colliculus
- medial vestibular nucleus
- entorhinal cortex
- perirhinal cortex
- neural layer of retina
- pyloric antrum
- dorsal tegmental nucleus
- right kidney
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 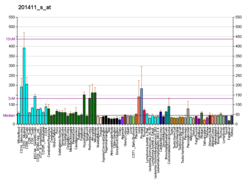
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding
| | Cellular component | - membrane
- recycling endosome membrane
- endosome
- integral component of membrane
| | Biological process | - regulation of cell differentiation
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001031706
NM_001100623
NM_001267062
NM_001267063
NM_001267064
|
|---|
NM_001267065
NM_001267066
NM_001267067
NM_001267068
NM_001309448
NM_001309450
NM_001309451
NM_001309452
NM_017958 |
| |
|---|
NM_145516
NM_175421
NM_001357425 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001094093
NP_001253991
NP_001253992
NP_001253993
NP_001253994
|
|---|
NP_001253995
NP_001253996
NP_001253997
NP_001296377
NP_001296379
NP_001296380
NP_001296381
NP_060428
NP_001094093.1 |
| |
|---|
NP_663491
NP_780630
NP_001344354 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 131.1 – 131.35 Mb | Chr 1: 34.89 – 34.92 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

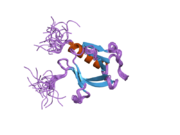 2dhi: Solution structure of the PH domain of Evectin-2 from mouse
2dhi: Solution structure of the PH domain of Evectin-2 from mouse