Human protein and coding gene
| PYCARD |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1UCP, 2KN6, 3J63, 5H8O |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | PYCARD, ASC, CARD5, TMS, TMS-1, TMS1, PYD and CARD domain containing |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 606838; MGI: 1931465; HomoloGene: 8307; GeneCards: PYCARD; OMA:PYCARD - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 16 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 16p11.2 | Start | 31,201,486 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 31,203,450 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7|7 F3 | Start | 127,588,880 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 127,593,039 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - monocyte
- granulocyte
- mucosa of transverse colon
- blood
- vulva
- human penis
- skin of leg
- skin of abdomen
- spleen
- gingival epithelium
|
| | Top expressed in | - Paneth cell
- migratory enteric neural crest cell
- ileum
- crypt of lieberkuhn of small intestine
- epithelium of small intestine
- duodenum
- large intestine
- colon
- left colon
- esophagus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein homodimerization activity
- interleukin-6 receptor binding
- BMP receptor binding
- protein binding
- identical protein binding
- enzyme binding
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- Pyrin domain binding
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process
- myosin I binding
- tropomyosin binding
- protease binding
- transmembrane transporter binding
- protein dimerization activity
- cysteine-type endopeptidase activity
| | Cellular component | - cytoplasm
- NLRP3 inflammasome complex
- NLRP1 inflammasome complex
- AIM2 inflammasome complex
- nucleolus
- endoplasmic reticulum
- mitochondrion
- IkappaB kinase complex
- nucleus
- secretory granule lumen
- azurophil granule lumen
- extracellular region
- cytosol
- protein-containing complex
- neuronal cell body
- Golgi membrane
- Golgi apparatus
- membrane
| | Biological process | - positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity
- regulation of apoptotic process
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator
- regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator
- positive regulation of adaptive immune response
- defense response to Gram-negative bacterium
- immune system process
- cellular response to tumor necrosis factor
- regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
- positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway
- positive regulation of JNK cascade
- negative regulation of interferon-beta production
- negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling
- myeloid dendritic cell activation
- positive regulation of T cell activation
- defense response to virus
- cellular response to interleukin-1
- positive regulation of apoptotic process
- positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production
- positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
- negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
- inflammatory response
- cellular response to lipopolysaccharide
- negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- signal transduction
- apoptotic process
- innate immune response
- neutrophil degranulation
- positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
- activation of innate immune response
- myeloid dendritic cell activation involved in immune response
- positive regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class II
- activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- positive regulation of actin filament polymerization
- regulation of protein stability
- positive regulation of interferon-gamma production
- positive regulation of interleukin-6 production
- positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation
- positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- macropinocytosis
- positive regulation of phagocytosis
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- positive regulation of T cell migration
- positive regulation of defense response to virus by host
- intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
- response to bacterium
- regulation of autophagy
- interleukin-1 beta production
- regulation of GTPase activity
- regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
- regulation of inflammatory response
- protein homooligomerization
- activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity
- negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response
- proteolysis
- positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_145183
NM_013258
NM_145182 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 31.2 – 31.2 Mb | Chr 7: 127.59 – 127.59 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
PYCARD, often referred to as ASC (Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PYCARD gene.[5] It is localized mainly in the nucleus of monocytes and macrophages. In case of pathogen infection, however, it relocalizes rapidly to the cytoplasm, perinuclear space, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria and it is a key adaptor protein in activation of the inflammasome.[6]
NMR structure of full-length ASC: PDB ID 2KN6 [1][7]
Function
This gene encodes an adaptor protein that is composed of two protein–protein interaction domains: a N-terminal PYRIN-PAAD-DAPIN domain (PYD) and a C-terminal caspase-recruitment domain (CARD). The PYD and CARD domains are members of the six-helix bundle death domain-fold superfamily that mediates assembly of large signaling complexes in the inflammatory and apoptotic signaling pathways via the activation of caspase. In normal cells, this protein is localized to the cytoplasm; however, in cells undergoing apoptosis, it forms ball-like aggregates near the nuclear periphery.
PYCARD can occur in four different isoforms. Isoform 1, often referred to as canonical PYCARD, and isoform 2 are the activatory isoforms. They co-localize with nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) and caspase-1. Unlike isoform 1, isoform 2 is involved in direct IL-1β processing regulation. Isoform 3 is an inhibitory isoform, so that it only co-localizes with caspase-1, but not with NLRs. Isoform 4 is not able to act as an adaptor protein in NLR signalling and its role remains elusive.[6]
Interactions
PYCARD has been shown to interact with MEFV.[8]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000103490 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030793 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PYCARD PYD and CARD domain containing". Retrieved 18 September 2010.
- ^ a b Dunn JH, Fujita M (2015). "PYCARD (PYD and CARD domain containing)". Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology (4). doi:10.4267/2042/56440 (inactive 2024-04-12). hdl:2042/56440. ISSN 1768-3262.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of April 2024 (link) - ^ Alba Ed (2009-11-20). "Structure and Interdomain Dynamics of Apoptosis-associated Speck-like Protein Containing a CARD (ASC)". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (47): 32932–32941. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.024273. ISSN 0021-9258. PMC 2781708. PMID 19759015.
- ^ Richards N, Schaner P, Diaz A, Stuckey J, Shelden E, Wadhwa A, Gumucio DL (October 2001). "Interaction between pyrin and the apoptotic speck protein (ASC) modulates ASC-induced apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (42): 39320–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104730200. PMID 11498534.
Further reading
- Masumoto J, Taniguchi S, Ayukawa K, Sarvotham H, Kishino T, Niikawa N, Hidaka E, Katsuyama T, Higuchi T, Sagara J (1999). "ASC, a novel 22-kDa protein, aggregates during apoptosis of human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (48): 33835–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.48.33835. PMID 10567338.
- Lee SK, Na SY, Jung SY, Choi JE, Jhun BH, Cheong J, Meltzer PS, Lee YC, Lee JW (2000). "Activating protein-1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and serum response factor as novel target molecules of the cancer-amplified transcription coactivator ASC-2". Mol. Endocrinol. 14 (6): 915–25. doi:10.1210/mend.14.6.0471. PMID 10847592.
- Conway KE, McConnell BB, Bowring CE, Donald CD, Warren ST, Vertino PM (2000). "TMS1, a novel proapoptotic caspase recruitment domain protein, is a target of methylation-induced gene silencing in human breast cancers". Cancer Res. 60 (22): 6236–42. PMID 11103776.
- McConnell BB, Vertino PM (2000). "Activation of a caspase-9-mediated apoptotic pathway by subcellular redistribution of the novel caspase recruitment domain protein TMS1". Cancer Res. 60 (22): 6243–7. PMID 11103777.
- Martinon F, Hofmann K, Tschopp J (2001). "The pyrin domain: a possible member of the death domain-fold family implicated in apoptosis and inflammation". Curr. Biol. 11 (4): R118-20. Bibcode:2001CBio...11.R118M. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00056-2. PMID 11250163. S2CID 18564343.
- Geddes BJ, Wang L, Huang WJ, Lavellee M, Manji GA, Brown M, Jurman M, Cao J, Morgenstern J, Merriam S, Glucksmann MA, DiStefano PS, Bertin J (2001). "Human CARD12 is a novel CED4/Apaf-1 family member that induces apoptosis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 284 (1): 77–82. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4928. PMID 11374873.
- Richards N, Schaner P, Diaz A, Stuckey J, Shelden E, Wadhwa A, Gumucio DL (2001). "Interaction between pyrin and the apoptotic speck protein (ASC) modulates ASC-induced apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (42): 39320–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104730200. PMID 11498534.
- Stimson KM, Vertino PM (2002). "Methylation-mediated silencing of TMS1/ASC is accompanied by histone hypoacetylation and CpG island-localized changes in chromatin architecture". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (7): 4951–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109809200. PMID 11733524.
- Manji GA, Wang L, Geddes BJ, Brown M, Merriam S, Al-Garawi A, Mak S, Lora JM, Briskin M, Jurman M, Cao J, DiStefano PS, Bertin J (2002). "PYPAF1, a PYRIN-containing Apaf1-like protein that assembles with ASC and regulates activation of NF-kappa B". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (13): 11570–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112208200. PMID 11786556.
- Srinivasula SM, Poyet JL, Razmara M, Datta P, Zhang Z, Alnemri ES (2002). "The PYRIN-CARD protein ASC is an activating adaptor for caspase-1". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (24): 21119–22. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200179200. PMID 11967258.
- Wang L, Manji GA, Grenier JM, Al-Garawi A, Merriam S, Lora JM, Geddes BJ, Briskin M, DiStefano PS, Bertin J (2002). "PYPAF7, a novel PYRIN-containing Apaf1-like protein that regulates activation of NF-kappa B and caspase-1-dependent cytokine processing". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (33): 29874–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203915200. PMID 12019269.
- Shiohara M, Taniguchi S, Masumoto J, Yasui K, Koike K, Komiyama A, Sagara J (2002). "ASC, which is composed of a PYD and a CARD, is up-regulated by inflammation and apoptosis in human neutrophils". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293 (5): 1314–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00384-4. PMID 12054656.
- Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J (2002). "The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta". Mol. Cell. 10 (2): 417–26. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00599-3. PMID 12191486.
- Stehlik C, Fiorentino L, Dorfleutner A, Bruey JM, Ariza EM, Sagara J, Reed JC (2002). "The PAAD/PYRIN-family protein ASC is a dual regulator of a conserved step in nuclear factor kappaB activation pathways". J. Exp. Med. 196 (12): 1605–15. doi:10.1084/jem.20021552. PMC 2196065. PMID 12486103.
- Moriai R, Tsuji N, Kobayashi D, Yagihashi A, Namiki Y, Takahashi H, Watanabe N (2003). "A proapoptotic caspase recruitment domain protein gene, TMS1, is hypermethylated in human breast and gastric cancers". Anticancer Res. 22 (6C): 4163–8. PMID 12553049.
- Dowds TA, Masumoto J, Chen FF, Ogura Y, Inohara N, Núñez G (2003). "Regulation of cryopyrin/Pypaf1 signaling by pyrin, the familial Mediterranean fever gene product". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 302 (3): 575–80. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00221-3. PMID 12615073.
- Masumoto J, Dowds TA, Schaner P, Chen FF, Ogura Y, Li M, Zhu L, Katsuyama T, Sagara J, Taniguchi S, Gumucio DL, Núñez G, Inohara N (2003). "ASC is an activating adaptor for NF-kappa B and caspase-8-dependent apoptosis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303 (1): 69–73. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00309-7. PMID 12646168.
- Stehlik C, Krajewska M, Welsh K, Krajewski S, Godzik A, Reed JC (2003). "The PAAD/PYRIN-only protein POP1/ASC2 is a modulator of ASC-mediated nuclear-factor-kappa B and pro-caspase-1 regulation". Biochem. J. 373 (Pt 1): 101–13. doi:10.1042/BJ20030304. PMC 1223462. PMID 12656673.
- Levine JJ, Stimson-Crider KM, Vertino PM (2003). "Effects of methylation on expression of TMS1/ASC in human breast cancer cells". Oncogene. 22 (22): 3475–88. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206430. PMID 12776200.
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 16 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

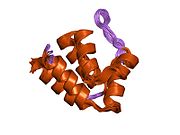 1ucp: NMR structure of the PYRIN domain of human ASC
1ucp: NMR structure of the PYRIN domain of human ASC



















