Pan Pan (kingdom)
Pan Pan | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd century CE–7th century CE | |||||||||
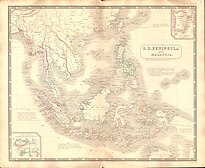
 Approximate location of Pan Pan. | |||||||||
| Capital | Unknown | ||||||||
| Common languages | Unknown | ||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Raja | |||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 3rd century CE | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 7th century CE | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Malaysia Thailand | ||||||||
Pan Pan or Panpan was a small Hindu kingdom believed to have existed around the 3rd to 7th century CE. It is believed to have been located on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula, with opinion varying from somewhere in Kelantan or Terengganu, in modern-day Malaysia[1] to the vicinity of Phunphin district, Surat Thani province, in modern Thailand.[2]
According to the Chinese text Jiu Tang Shu, Pan Pan was bordered in the south with Langkasuka,[1]: 53 and in the north with Tun Sun near the Kra Isthmus.[3]: 259 Jacq-Hergoualc'h speculates that the border may have been south of Nakhon Si Thammarat, possibly near Songkhla.[1]: 53
After the northern neighbor Tun Sun gained independence from Funan and became Lang-chia or Lang-ya-hsiu in the late 5th century CE, its southern part joined Pan Pan in the 6th century,[3]: 262–263 while the northern territory became Dvaravati.[3]: 268–269
It is speculated to be related to the Patani Kingdom, which occupied the same area many centuries later, and has some differences in culture and language to other Malay regions nearby.
History
Little is known about this kingdom.
Pan Pan sent its first missions to the Chinese Liu Song dynasty between 424 CE nad 453[4]: 52 From here, Kaundinya II is said to have tried to re-introduce Hinduism to the Kingdom of Funan on the other side of the Gulf of Siam.[5]
Pan Pan sent tribute to the Liang dynasty and the Chen dynasty of China. in 529, 533, 534, 535 and 571[6] In 616 and 637, Pan Pan sent tribute to the Chinese Tang dynasty.[7]
The kingdom was later conquered by Srivijaya under the leadership of Dharmasetu before 775.[8]
Though rare, archeological discoveries show evidence of a lively economic flowering in the region through international maritime trade.[9]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Dougald J. W. O'Reilly (2007). Early Civilizations of Southeast Asia. Rowman Altamira. ISBN 978-0-7591-0279-8.
- ^ Joachim Schliesinger (2016). Origin of Man in Southeast Asia 3 Volume 3: Indianization and the Temples of the Mainland; Part 3 Pre-Modern Thailand, Laos and Burma. Booksmango. ISBN 978-1633237278.
- ^ a b c Lawrence Palmer Briggs (1950). "The Khmer Empire and the Malay Peninsula". The Far Eastern Quarterly. 9 (3). Duke University Press: 256–305. doi:10.2307/2049556. JSTOR 2049556. Archived from the original on 26 April 2024.
- ^ Coedès, George (1968). Walter F. Vella (ed.). The Indianized States of Southeast Asia. trans.Susan Brown Cowing. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-0368-1.
- ^ Hall, D.G.E. (1981). A History of South-East Asia, Fourth Edition. Hong Kong: Macmillan Education Ltd. p. 38. ISBN 0-333-24163-0.
- ^ Annals of Liang dynasty. Annals of Chen dynasty
- ^ Annal of Tang dynasty. Foreign countries at the South.
- ^ Munoz, Paul Michel (2006). Early Kingdoms of the Indonesian Archipelago and the Malay Peninsula. Singapore: Editions Didier Millet. pp. 130–131. ISBN 981-4155-67-5.
- ^ Jacq-Hergoualc'h, Micheal (2002). The Malay Peninsula: Crossroads of the Maritime Silk-Road (100 Bc-1300 Ad). BRILL. pp. 158–159. ISBN 978-90-04-11973-4.