| SRSF11 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SRSF11, NET2, SFRS11, dJ677H15.2, p54, serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 11, serine and arginine rich splicing factor 11 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 602010; MGI: 1916457; HomoloGene: 36164; GeneCards: SRSF11; OMA:SRSF11 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1p31.1 | Start | 70,205,682 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 70,253,052 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 3 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 3|3 H4 | Start | 158,010,473 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 158,036,639 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - visceral pleura
- parietal pleura
- tibia
- mucosa of paranasal sinus
- gastric mucosa
- Achilles tendon
- endothelial cell
- skin of hip
- sural nerve
- germinal epithelium
|
| | Top expressed in | - neural layer of retina
- tail of embryo
- genital tubercle
- abdominal wall
- cerebellar cortex
- saccule
- primitive streak
- dermis
- vas deferens
- superior frontal gyrus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 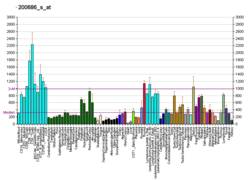
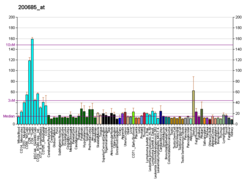 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- nucleic acid binding
- RNA binding
| | Cellular component | - nucleus
- nucleoplasm
- nuclear speck
| | Biological process | - mRNA splicing, via spliceosome
- termination of RNA polymerase II transcription
- mRNA processing
- mRNA 3'-end processing
- mRNA export from nucleus
- RNA splicing
- RNA export from nucleus
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001190987
NM_004768
NM_001350605
NM_001350606
NM_001350607
|
|---|
NM_001350608
NM_001350609
NM_001350610
NM_001350611
NM_001350612
NM_001350613
NM_001350614
NM_001350615
NM_001350616
NM_001394402
NM_001394403
NM_001394404
NM_001394405
NM_001394406
NM_001394407
NM_001394408 |
| |
|---|
NM_001093752
NM_001093753
NM_026989
NM_001356997 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001177916
NP_004759
NP_001337534
NP_001337535
NP_001337536
|
|---|
NP_001337537
NP_001337538
NP_001337539
NP_001337540
NP_001337541
NP_001337542
NP_001337543
NP_001337544
NP_001337545 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 70.21 – 70.25 Mb | Chr 3: 158.01 – 158.04 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|




















