Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| SUB1 |
|---|
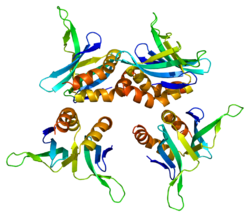 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1PCF, 2C62, 2PHE, 4USG |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SUB1, P15, PC4, p14, SUB1 homolog, transcriptional regulator, SUB1 regulator of transcription |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600503; MGI: 104811; HomoloGene: 38218; GeneCards: SUB1; OMA:SUB1 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 5 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 5p13.3 | Start | 32,531,633 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 32,604,079 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 15 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 15|15 A1 | Start | 11,981,425 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 11,997,069 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - epithelium of nasopharynx
- lactiferous duct
- epithelium of colon
- ganglionic eminence
- gingival epithelium
- parotid gland
- bone marrow cells
- germinal epithelium
- endometrium
- ventricular zone
|
| | Top expressed in | - genital tubercle
- tail of embryo
- yolk sac
- abdominal wall
- primitive streak
- neural tube
- gastrula
- medial ganglionic eminence
- migratory enteric neural crest cell
- embryo
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 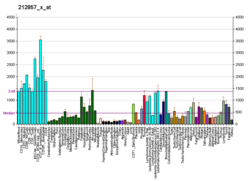
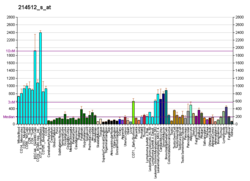
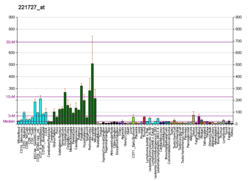 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - single-stranded DNA binding
- DNA binding
- transcription coactivator activity
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- protein binding
- RNA binding
- identical protein binding
- sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding
| | Cellular component | - nucleolus
- extracellular exosome
- transcription regulator complex
- nucleus
| | Biological process | - regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- transcription by RNA polymerase II
- SMAD protein signal transduction
- transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 5: 32.53 – 32.6 Mb | Chr 15: 11.98 – 12 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Activated RNA polymerase II transcriptional coactivator p15 also known as positive cofactor 4 (PC4) or SUB1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SUB1 gene.[5][6][7] The human SUB1 gene[7] is named after an orthologous gene in yeast.[8]
SUB1 is induced by oxidative stress, and is involved in coordinating cellular responses to DNA strand breaks that arise after oxidative stress.Yu L, Ma H, Ji X, Volkert MR (January 2016). "The Sub1 nuclear protein protects DNA from oxidative damage". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 412 (1–2): 165–171. doi:10.1007/s11010-015-2621-x. PMC 5064834. PMID 26708217. Yeast SUB1 has structural and functional similarities to human alpha-synuclein, a protein that has an important role in Parkinson's disease.Schaser AJ, Osterberg VR, Dent SE, Stackhouse TL, Wakeham CM, Boutros SW, et al. (July 2019). "Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 10919. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47227-z. PMC 6662836. PMID 31358782. Like SUB1, alpha-synuclein functions in regulating DNA repair including repair of DNA double-strand breaks.
Interactions
SUB1 has been shown to interact with CSTF2.[9]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000113387 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022205 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kretzschmar M, Kaiser K, Lottspeich F, Meisterernst M (August 1994). "A novel mediator of class II gene transcription with homology to viral immediate-early transcriptional regulators". Cell. 78 (3): 525–534. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90429-4. PMID 8062392. S2CID 29077941.
- ^ Ge H, Roeder RG (August 1994). "Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes". Cell. 78 (3): 513–523. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90428-6. PMID 8062391. S2CID 1140379.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene SUB1: SUB1 homolog (S. cerevisiae)".
- ^ Knaus R, Pollock R, Guarente L (April 1996). "Yeast SUB1 is a suppressor of TFIIB mutations and has homology to the human co-activator PC4". The EMBO Journal. 15 (8): 1933–1940. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00544.x. PMC 450112. PMID 8617240.
- ^ Calvo O, Manley JL (May 2001). "Evolutionarily conserved interaction between CstF-64 and PC4 links transcription, polyadenylation, and termination". Molecular Cell. 7 (5): 1013–1023. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00236-2. PMID 11389848.
Further reading
- Kaiser K, Stelzer G, Meisterernst M (July 1995). "The coactivator p15 (PC4) initiates transcriptional activation during TFIIA-TFIID-promoter complex formation". The EMBO Journal. 14 (14): 3520–3527. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07358.x. PMC 394420. PMID 7628453.
- Ge H, Zhao Y, Chait BT, Roeder RG (December 1994). "Phosphorylation negatively regulates the function of coactivator PC4". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (26): 12691–12695. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.26.12691. PMC 45505. PMID 7809103.
- Brandsen J, Werten S, van der Vliet PC, Meisterernst M, Kroon J, Gros P (November 1997). "C-terminal domain of transcription cofactor PC4 reveals dimeric ssDNA binding site". Nature Structural Biology. 4 (11): 900–903. doi:10.1038/nsb1197-900. PMID 9360603. S2CID 30710386.
- Malik S, Guermah M, Roeder RG (March 1998). "A dynamic model for PC4 coactivator function in RNA polymerase II transcription". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (5): 2192–2197. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95.2192M. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.5.2192. PMC 19292. PMID 9482861.
- Luo Y, Ge H, Stevens S, Xiao H, Roeder RG (July 1998). "Coactivation by OCA-B: definition of critical regions and synergism with general cofactors". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 18 (7): 3803–3810. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.7.3803. PMC 108964. PMID 9632764.
- Currie RA (July 1998). "Biochemical characterization of the NF-Y transcription factor complex during B lymphocyte development". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (29): 18220–18229. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.29.18220. PMID 9660784.
- Wang Z, Roeder RG (April 1998). "DNA topoisomerase I and PC4 can interact with human TFIIIC to promote both accurate termination and transcription reinitiation by RNA polymerase III". Molecular Cell. 1 (5): 749–757. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80074-X. PMID 9660958.
- Holloway AF, Occhiodoro F, Mittler G, Meisterernst M, Shannon MF (July 2000). "Functional interaction between the HIV transactivator Tat and the transcriptional coactivator PC4 in T cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (28): 21668–21677. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909058199. PMID 10887206.
- Yuan CX, Gurley WB (July 2000). "Potential targets for HSF1 within the preinitiation complex". Cell Stress & Chaperones. 5 (3): 229–242. PMC 312889. PMID 11005381.
- Kumar BR, Swaminathan V, Banerjee S, Kundu TK (May 2001). "p300-mediated acetylation of human transcriptional coactivator PC4 is inhibited by phosphorylation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (20): 16804–16809. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100934200. PMID 11279157.
- Yu P, Huang B, Shen M, Lau C, Chan E, Michel J, et al. (January 2001). "p15(PAF), a novel PCNA associated factor with increased expression in tumor tissues". Oncogene. 20 (4): 484–489. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204113. PMID 11313979. S2CID 39144360.
- Calvo O, Manley JL (May 2001). "Evolutionarily conserved interaction between CstF-64 and PC4 links transcription, polyadenylation, and termination". Molecular Cell. 7 (5): 1013–1023. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00236-2. PMID 11389848.
- Dubois T, Zemlickova E, Howell S, Aitken A (February 2003). "Centaurin-alpha 1 associates in vitro and in vivo with nucleolin". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 301 (2): 502–508. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)03010-3. PMID 12565890.
- Fukuda A, Tokonabe S, Hamada M, Matsumoto M, Tsukui T, Nogi Y, Hisatake K (April 2003). "Alleviation of PC4-mediated transcriptional repression by the ERCC3 helicase activity of general transcription factor TFIIH". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (17): 14827–14831. doi:10.1074/jbc.M213172200. PMID 12590132.
- Swietlicki E, Iordanov H, Fritsch C, Yi L, Levin MS, Rubin DC (2003). "Growth factor regulation of PC4/TIS7, an immediate early gene expressed during gut adaptation after resection". Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 27 (2): 123–131. doi:10.1177/0148607103027002123. PMID 12665168.
- Banerjee S, Kumar BR, Kundu TK (March 2004). "General transcriptional coactivator PC4 activates p53 function". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (5): 2052–2062. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.5.2052-2062.2004. PMC 350566. PMID 14966284.
- Caldwell RB, Braselmann H, Schoetz U, Heuer S, Scherthan H, Zitzelsberger H (July 2016). "Positive Cofactor 4 (PC4) is critical for DNA repair pathway re-routing in DT40 cells". Scientific Reports. 6: 28890. Bibcode:2016NatSR...628890C. doi:10.1038/srep28890. PMC 4931448. PMID 27374870.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P53999 (Activated RNA polymerase II transcriptional coactivator p15) at the PDBe-KB.
PDB gallery
-
1pcf: HUMAN TRANSCRIPTIONAL COACTIVATOR PC4 C-TERMINAL DOMAIN -
2c62: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN TRANSCRIPTION COFACTOR PC4 IN COMPLEX WITH SINGLE-STRANDED DNA -
2phe: Model for VP16 binding to PC4 |
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 5 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

 1pcf: HUMAN TRANSCRIPTIONAL COACTIVATOR PC4 C-TERMINAL DOMAIN
1pcf: HUMAN TRANSCRIPTIONAL COACTIVATOR PC4 C-TERMINAL DOMAIN 2c62: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN TRANSCRIPTION COFACTOR PC4 IN COMPLEX WITH SINGLE-STRANDED DNA
2c62: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN TRANSCRIPTION COFACTOR PC4 IN COMPLEX WITH SINGLE-STRANDED DNA 2phe: Model for VP16 binding to PC4
2phe: Model for VP16 binding to PC4























