GMP synthase
GMP synthase
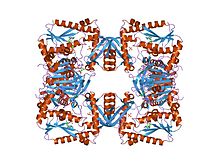
GMP synthase de Streptomyces aureofaciens (PDB 1GMP)
| N° EC | EC 6.3.5.2 |
|---|---|
| N° CAS | 37318-71-1 |
| IUBMB | Entrée IUBMB |
|---|---|
| IntEnz | Vue IntEnz |
| BRENDA | Entrée BRENDA |
| KEGG | Entrée KEGG |
| MetaCyc | Voie métabolique |
| PRIAM | Profil |
| PDB | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBj PDBsum |
| GO | AmiGO / EGO |
modifier 
La GMP synthase est une ligase qui catalyse la réaction :
Cette enzyme intervient dans la biosynthèse des nucléotides à guanine à partir de l'IMP. Elle fonctionne en deux étapes successives :
- L-glutamine + H2O L-glutamate + NH3 ;
- ATP + XMP + NH3 AMP + pyrophosphate + GMP.
Elle est présente chez tous les êtres vivants, où elle joue un rôle essentiel dans la formation du GTP et de l'ATP, nucléotides essentiels aussi bien dans le métabolisme énergétique des cellules que dans leur matériel génétique comme précurseurs des acides nucléiques.
Notes et références
- (en) Ulf Lagerkvist, « Biosynthesis of guanosine 5'-phosphate. II. Amination of xanthosine 5'-phosphate by purified enzyme from pigeon liver », Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 233, no 1, , p. 143-149 (PMID 13563458, lire en ligne)
- (en) Richard Abrams et Marian Bentley, « Biosynthesis of nucleic acid purines. III. Guanosine 5′-phosphate formation from xanthosine 5′-phosphate and l-glutamine », Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, vol. 79, , p. 91-110 (DOI 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90383-2, lire en ligne)
- (en) H. Zalkin, P. Argos, S. V. Narayana, A. A. Tiedeman et J. M. Smith, « Identification of a trpG-related glutamine amide transfer domain in Escherichia coli GMP synthetase », Journal of Biochemical Chemistry, vol. 260, no 6, , p. 3350-3354 (PMID 2982857, lire en ligne)
- (en) Jessica L. Abbott, Jordan M. Newell, Christine M. Lightcap, Mary E. Olanich, Danielle T. Loughlin, Melanie A. Weller, Gary Lam, Sidney Pollack et Walter A. Patton, « The Effects of Removing the GAT Domain from E. coli GMP Synthetase », The Protein Journal, vol. 25, nos 7-8, , p. 483-491 (PMID 17103135, DOI 10.1007/s10930-006-9032-5, lire en ligne)
 Portail de la biochimie
Portail de la biochimie