| TEK |
|---|
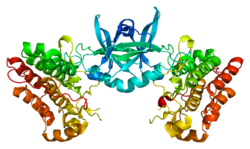 |
| Structure de la protéine TEK. Basé sur l'identification PDB 1fvr. |
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
4K0V, 1FVR, 2GY5, 2GY7, 2OO8, 2OSC, 2P4I, 2WQB, 3L8P, 4X3J |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | TEK, TIE-2, Tie-2 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 600221 MGI: 98664 HomoloGene: 397 GeneCards: TEK |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 9 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 9p21.2 | Début | 27,109,141 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 27,230,174 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 4 C5|4 43.34 cM | Début | 94,627,526 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 94,763,213 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
| Fortement exprimé dans | - poumon droit
- pleura viscéral
- upper lobe of left lung
- ovocyte
- parietal pleura
- secondary oocyte
- lobe inférieur du poumon
- subcutaneous adipose tissue
- metanephric glomerulus
- placenta
|
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - Vasculature of brain
- poumon droit
- lobe pulmonaire droit
- poumon gauche
- atrium
- left lung lobe
- valve auriculo-ventriculaire
- valve sigmoïde
- valve aortique
- endocardial cushion
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - activité de transférase
- protein kinase activity
- liaison nucléotide
- activité kinase
- liaison protéique
- transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity
- protein tyrosine kinase activity
- liaison ATP
- signaling receptor activity
- growth factor binding
- Récepteurs à activité tyrosine kinase
- transmembrane signaling receptor activity
| | Composant cellulaire | - cytoplasme
- integral component of membrane
- membrane
- jonction cellule-cellule
- focal adhesion
- integral component of plasma membrane
- stress fiber
- région extracellulaire
- microvillosité
- surface cellulaire
- basal plasma membrane
- jonction cellulaire
- basolateral plasma membrane
- apical plasma membrane
- filament d'actine
- radeau lipidique
- cytosquelette
- Centre organisateur des microtubules
- membrane plasmique
- receptor complex
| | Processus biologique | - negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process
- positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling
- positive regulation of protein phosphorylation
- response to hypoxia
- positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation
- heart trabecula formation
- phosphorylation
- transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway
- regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process
- cell-cell signaling
- response to peptide hormone
- sprouting angiogenesis
- negative regulation of apoptotic process
- ossification endochondrale
- positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction
- response to organic substance
- positive regulation of angiogenesis
- MAPK cascade
- positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity
- positive regulation of endothelial cell migration
- réaction à l'œstrogène
- développement du cœur
- regulation of vascular permeability
- phosphorylation des protéines
- protein complex oligomerization
- endothelial cell proliferation
- angiogenèse
- Tie signaling pathway
- positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- negative regulation of angiogenesis
- protein autophosphorylation
- positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly
- regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity
- positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
- peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
- substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading
- response to cAMP
- definitive hemopoiesis
- positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization
- negative regulation of inflammatory response
- leukocyte migration
- transduction de signal
- glomerulus vasculature development
- negative regulation of signal transduction
- différenciation cellulaire
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_000459
NM_001290077
NM_001290078
NM_001375475
NM_001375476 |
| |
|---|
NM_001290549
NM_001290551
NM_013690 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | |
|---|
NP_000450
NP_001277006
NP_001277007
NP_001362404
NP_001362405 |
| |
|---|
NP_001277478
NP_001277480
NP_038718 |
|
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 9: 27.11 – 27.23 Mb | Chr 4: 94.63 – 94.76 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|
Le TIE2 (pour l'anglais tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin and EGF homology domains), ou TEK, est avec le TIE1 un des deux récepteurs des cellules endothéliales, et est impliqué dans le contrôle de l'angiogénèse. C'est un récepteur aux angiopoïétines Ang-1 et Ang-2. Son gène est le TEK situé sur le chromosome 9 humain.
Rôle
Ce récepteur possède une activité de tyrosine kinase et se lie à l'angiopoïétine 1[5]. Il est exprimé sur des monocytes qui interviennent dans l'angiogenèse[6].
Stimulée par l'angiopoïétine, ce récepteur, situé sur les cellules souches hématopoïétiques, permet la mise au repos de celles-ci et leur fixation au niveau de la moelle osseuse[7].
En médecine
Une mutation du gène TEK entraînant une augmentation de l'activité du TIE2 est responsable d'une malformations veineuses muqueuses et cutanées familiale[8]. D'autres mutations, entraînant cette fois ci la formation d'une molécule inactive, cause un syndrome héréditaire semblable[9]. En dehors des formes familiales, des variants du TIE2 sont responsables de près de la moitié des cas sporadiques de malformations veineuses[10].
Notes et références
- ↑ a b et c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000120156 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ a b et c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000006386 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning, Cell, 1996;87:1161–1169
- ↑ De Palma M, Venneri MA, Galli R et al. Tie2 identifies a hematopoietic lineage of proangiogenic monocytes required for tumor vessel formation and a mesenchymal population of pericyte progenitors, Cancer Cell, 2005;8:211–226
- ↑ Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M et al. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche, Cell, 2004;118:149–161
- ↑ Vikkula M, Boon LM, Carraway KL 3rd et al. Vascular dysmorphogenesis caused by an activating mutation in the receptor tyrosine kinase TIE2, Cell, 1996;87:1181–1190
- ↑ Limaye N, Wouters V, Uebelhoer M et al. Somatic mutations in angiopoietin receptor gene TEK cause solitary and multiple sporadic venous malformations, Nat Genet, 2009;41:118–124
- ↑ Soblet J, Limaye N, Uebelhoer M, Boon LM, Vikkula M, Variable somatic TIE2 mutations in half of sporadic venous malformations, Mol Syndromol, 2013;4:179–183
 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire

 Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine  Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire 


















