FRS3
| FRS3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identificadores | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomes alternativos | FRS3, Substrato receptor 3 do fator de crescimento de fibroblastos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
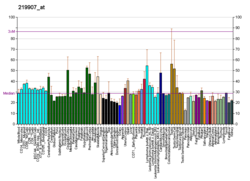
| IDs externos | OMIM: 607744 HomoloGene: 4845 GeneCards: FRS3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Substrato receptor 3 do fator de crescimento de fibroblastos é uma proteína que em humanos é codificada pelo gene FRS3.[2][3][4] A proteína codificada por esse gene é um substrato para o receptor do fator de crescimento de fibroblastos. É encontrado na membrana plasmática periférica e funciona na ligação da estimulação do receptor FGF aos ativadores de Ras.[4]
Referências
- ↑ «Human PubMed Reference:»
- ↑ Wang JK, Xu H, Li HC, Goldfarb M (outubro de 1996). «Broadly expressed SNT-like proteins link FGF receptor stimulation to activators of Ras». Oncogene. 13 (4): 721–9. PMID 8761293
- ↑ Xu H, Lee KW, Goldfarb M (agosto de 1998). «Novel recognition motif on fibroblast growth factor receptor mediates direct association and activation of SNT adapter proteins». J Biol Chem. 273 (29): 17987–90. PMID 9660748. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.29.17987
- ↑ a b «Entrez Gene: FRS3 fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 3»
Leitura adicional
- Lim YP, Low BC, Lim J, et al. (1999). «Association of atypical protein kinase C isotypes with the docker protein FRS2 in fibroblast growth factor signaling.». J. Biol. Chem. 274 (27): 19025–34. PMID 10383403. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.19025
- Ong SH, Guy GR, Hadari YR, et al. (2000). «FRS2 proteins recruit intracellular signaling pathways by binding to diverse targets on fibroblast growth factor and nerve growth factor receptors.». Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (3): 979–89. PMC 85215
 . PMID 10629055. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.979-989.2000
. PMID 10629055. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.979-989.2000 - Yamada M, Suzuki K, Mizutani M, et al. (2001). «Analysis of tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent protein-protein interactions in TrkB-mediated intracellular signaling using modified yeast two-hybrid system.». J. Biochem. 130 (1): 157–65. PMID 11432792. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002955
- Yan KS, Kuti M, Yan S, et al. (2002). «FRS2 PTB domain conformation regulates interactions with divergent neurotrophic receptors.». J. Biol. Chem. 277 (19): 17088–94. PMID 11877385. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107963200
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). «Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.». Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899 - Ranzi V, Meakin SO, Miranda C, et al. (2003). «The signaling adapters fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 and 3 are activated by the thyroid TRK oncoproteins.». Endocrinology. 144 (3): 922–8. PMID 12586769. doi:10.1210/en.2002-221002
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). «The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6.». Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. PMID 14574404. doi:10.1038/nature02055
- Gotoh N, Laks S, Nakashima M, et al. (2004). «FRS2 family docking proteins with overlapping roles in activation of MAP kinase have distinct spatial-temporal patterns of expression of their transcripts.». FEBS Lett. 564 (1-2): 14–8. PMID 15094036. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00287-X
- Hassel S, Eichner A, Yakymovych M, et al. (2004). «Proteins associated with type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMPR-II) and identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry.». Proteomics. 4 (5): 1346–58. PMID 15188402. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300770
- Huang L, Gotoh N, Zhang S, et al. (2004). «SNT-2 interacts with ERK2 and negatively regulates ERK2 signaling in response to EGF stimulation.». Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 324 (3): 1011–7. PMID 15485655. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.152
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). «The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).». Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504 - Harada A, Katoh H, Negishi M (2005). «Direct interaction of Rnd1 with FRS2 beta regulates Rnd1-induced down-regulation of RhoA activity and is involved in fibroblast growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.». J. Biol. Chem. 280 (18): 18418–24. PMID 15738000. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411356200
- Huang L, Watanabe M, Chikamori M, et al. (2006). «Unique role of SNT-2/FRS2beta/FRS3 docking/adaptor protein for negative regulation in EGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathways.». Oncogene. 25 (49): 6457–66. PMID 16702953. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209656
 | Este artigo sobre Genética é um esboço. Você pode ajudar a Wikipédia expandindo-o.
|
 Portal da genética
Portal da genética Portal da bioquímica
Portal da bioquímica